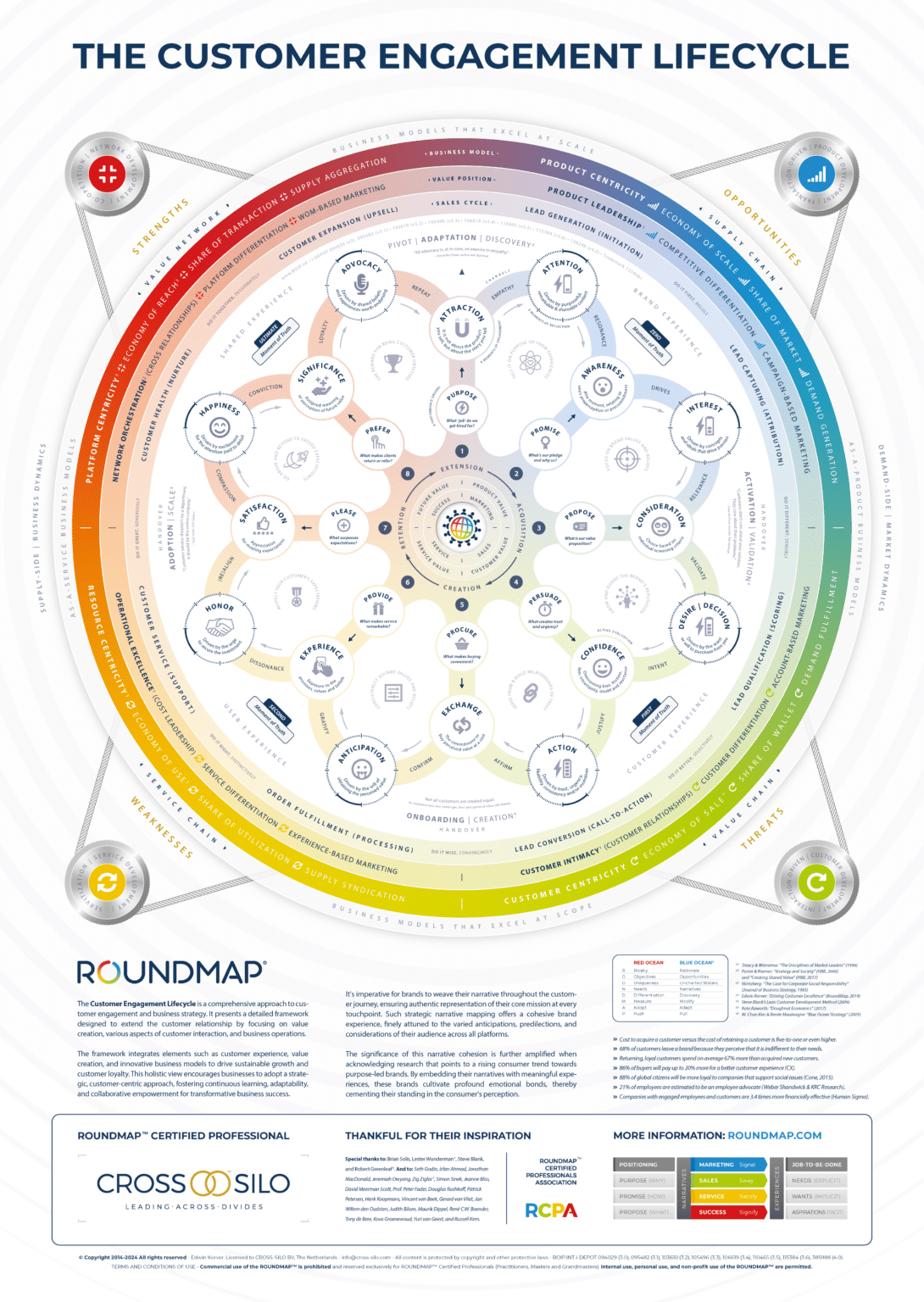
The Customer Engagement Lifecycle represents a pivotal step in understanding and optimizing the entire frontend operation of a business. This lifecycle assesses every interaction between the company and its customers, serving as the foundation for RoundMap’s broader, unified framework. By dissecting and analyzing customer engagement at each touchpoint, it laid the groundwork for developing a whole-system approach to business orchestration.
As a subset of the Network Orchestration Lifecycle, the Customer Engagement Lifecycle operates alongside the Value Orchestration Lifecycle and the principles of Shared Value. Together, these components drive meaningful relationships with all relevant stakeholders, ensuring that value is continually co-created, shared, and amplified across an ecosystem of partners. This lifecycle is critical in building Shared Value Networks—networks that not only serve the customer but also foster long-term, sustainable success for all stakeholders.
Revenue Engine
- Lead Generation: The revenue engine starts with attracting potential customers or leads to the business. This can involve marketing activities such as advertising, content creation, search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and lead generation campaigns.
- Lead Nurturing: Once leads are generated, the revenue engine focuses on nurturing those leads and building relationships. This includes activities such as lead scoring, lead qualification, personalized communication, and targeted marketing campaigns to move leads through the sales funnel.
- Sales Process: The revenue engine incorporates a well-defined sales process to convert leads into paying customers. This may involve prospecting, needs analysis, presentations, negotiation, and closing deals. Sales teams often use customer relationship management (CRM) systems to track and manage sales processes.
- Customer Retention and Upselling: A revenue engine recognizes the importance of customer retention and driving additional revenue from existing customers. It includes strategies and initiatives to foster customer loyalty, provide excellent customer service, and identify upselling or cross-selling opportunities.
- Metrics and Analytics: An effective revenue engine relies on data and analytics to track performance, measure key metrics, and make data-driven decisions. This may involve monitoring conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, lifetime value, and other relevant KPIs to optimize revenue generation efforts.
- Continuous Improvement: A revenue engine is an iterative and dynamic process that constantly seeks to improve performance. It involves analyzing results, identifying areas of improvement, testing new strategies, and refining the revenue generation approach based on feedback and insights.
Overall, a revenue engine is a holistic approach that aligns sales, marketing, and success efforts to generate revenue for an organization. It focuses on integrating various components of the revenue generation process and optimizing them to drive sustainable growth and financial success.
Building A Resilient Revenue Engine
- Diversify Revenue Streams: To mitigate the impact of cyclical fluctuations, it is essential to diversify revenue streams. Explore opportunities to offer complementary products or services that cater to different market segments or industries. This can help balance revenue generation during various phases of the business cycle.
- Market Research and Forecasting: Stay informed about market trends, industry forecasts, and economic indicators. Conduct regular market research to anticipate changes in customer demand and adjust your revenue generation strategies accordingly. This can help you proactively respond to cyclical fluctuations and identify growth opportunities.
- Flexibility in Pricing and Packaging: Consider offering flexible pricing and packaging options to adapt to changing market conditions. During downturns or slower periods, explore options such as discounts, promotional offers, or bundling products/services to incentivize customers and maintain revenue flow. Assess the market demand and adjust pricing to capture additional value during upswings.
- Customer Retention and Upselling: Build strong customer bonds to foster loyalty and retention. During cyclical downturns, prioritize customer retention efforts to maintain a steady revenue base. Additionally, identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling to existing customers, as they will likely be more receptive to additional products or services.
- Agile Marketing and Sales Strategies: Adopt agile marketing and sales strategies that allow flexibility and quick adjustments to changing market dynamics. Monitor market trends, customer needs, and competitor activities to adapt your messaging, target audience, and marketing channels as required. Align your sales team’s efforts with changing market conditions and equip them with the skills and tools necessary to pivot their approach.
- Financial Planning and Reserves: Establish a robust financial planning process considering cyclical fluctuations. Build reserves during peak periods to help sustain operations during downturns. This ensures financial stability and allows you to continue investing in revenue-generating activities even during challenging times.
- Continuous Improvement and Innovation: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within your organization. Encourage employees to contribute ideas, identify new revenue streams, and explore ways to enhance existing products or services. This mindset allows you to adapt to cyclical changes, seize new opportunities, and stay ahead of the competition.
By incorporating these strategies into your revenue engine, you can create a more resilient and continuous revenue generation process that navigates the dynamics of cyclical management. It enables your business to thrive throughout different business cycle phases and enhances your long-term sustainability.