The Planned Impact Model is built upon a simple but powerful idea: that businesses can create a positive impact by aligning their goals and operations with their impact goals, taking deliberate action, and actively seeking opportunities to make a difference. By incorporating impact measurement and management into their operations, businesses can create positive change, differentiate themselves from their competitors, and improve their long-term performance.
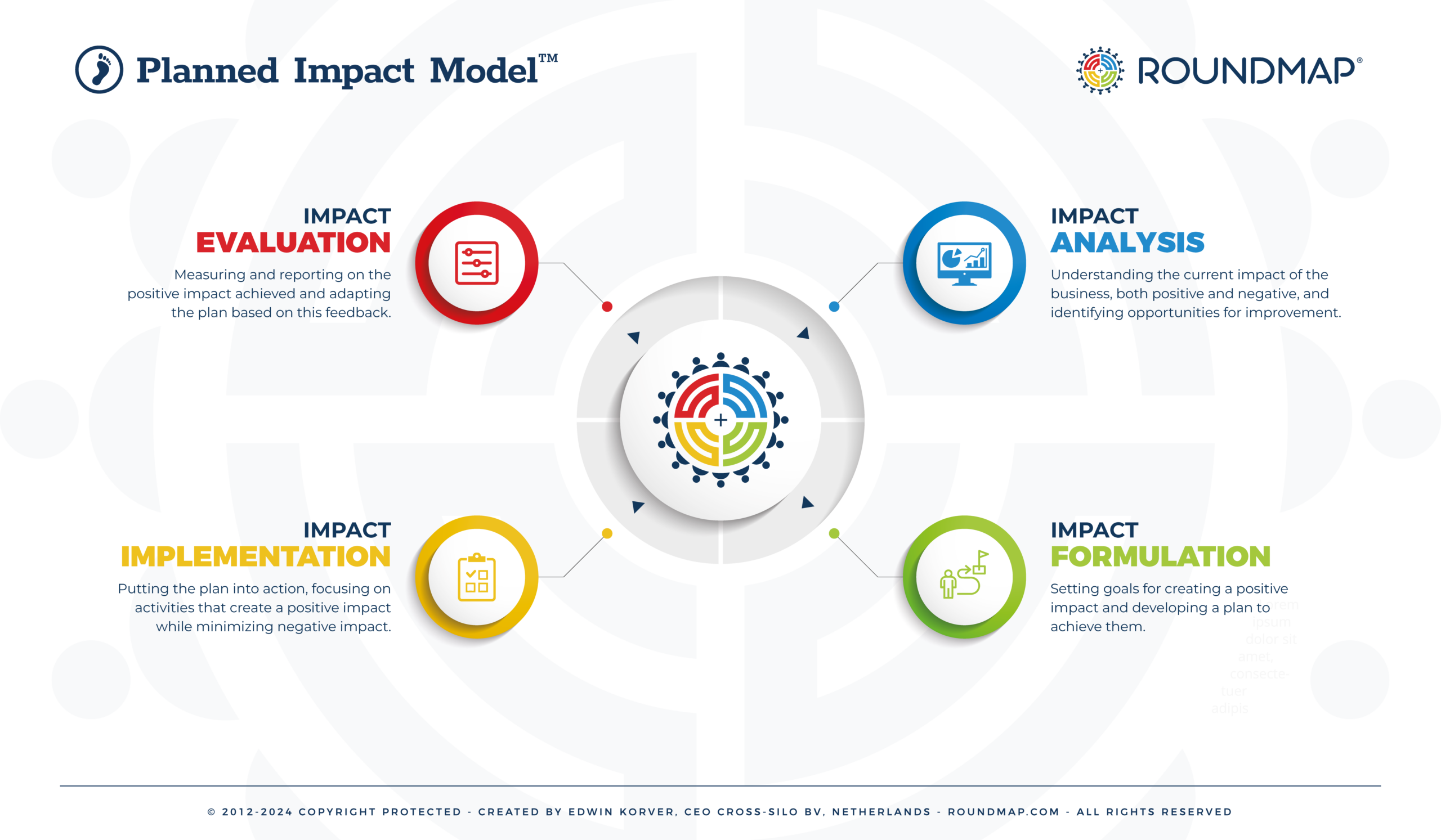
The Impact Planning Process within the RoundMap® framework consists of four iterative steps:
- Impact Analysis: Understanding the current impact of the business, both positive and negative, and identifying opportunities for improvement.
- Impact Formulation: Setting goals for creating a positive impact and developing a plan to achieve them.
- Impact Implementation: Putting the plan into action, focusing on activities that create a positive impact while minimizing negative impact.
- Impact Evaluation: Measuring and reporting on the positive impact achieved and adapting the plan based on this feedback.
The Planned Impact Model is an integral part of the business strategy; it must be perceived as a living, breathing thing that requires constant evaluation and adaptation. It’s like a well-oiled machine that needs regular maintenance to keep running smoothly.
Plan For Impact
Let’s look the following scheme, representing the four steps of the Impact Planning Process:
Planned Impact through Participative Engagement (PIPE)
As indicated by the success story of Panera Bread, to build a meaningful impact business model, you’ll need to engage with your customers to learn what it is they value, motivate and inspire your employees to bring that value to fruition, and appeal to investors that seek long-term sustainable growth.
By incorporating impact planning into the business model, companies can move beyond words and take concrete actions toward achieving their mission and purpose. This approach helps companies to identify the key stakeholders, understand their needs, and develop strategies that address their concerns.
Edwin Korver: “Within the RoundMap® framework, the Planned Impact through Participative Engagement (PIPE) approach is vital for bringing your Planned Impact Model to life. PIPE embodies ethos in action, focusing on engaging the entire human system within your company. This approach ensures that the impact objectives are not just organizational mandates but become integral to the collective effort of every team member. With PIPE, impact goals transform from abstract ideas into concrete, collaborative achievements, ensuring the path to success is paved with shared commitment and purposeful action.”
Plan For Impact Form
Here’s what a simple form could look like to consider the strategic imperatives of planning for impact:
Impact Dimensions
- Environmental Footprint ─ What actions can we take to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability?
- Governance and Ethics ─ How effectively are we ensuring ethical behavior and transparent governance throughout our organization?
- Social Impact ─ What initiatives can we implement to positively contribute to the social well-being of our stakeholders and communities?
- Financial Impact ─ How do our activities and decisions impact our financial performance and value creation?
- Supply Chain Management ─ How can we strengthen and optimize our supply chain to enhance sustainability and responsibly manage risks?
- Stakeholder Engagement ─ How are we actively engaging and addressing the needs and perspectives of our stakeholders?
- Innovation ─ What innovative approaches can we adopt to drive positive change and address emerging challenges?
- Technology and Digitalization ─ How can we leverage technology and digital solutions to enhance our impact and efficiency?
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion ─ What steps can we take to foster diversity, equity, and inclusion within our organization and beyond?
- Customer Experience and Engagement ─ How can we improve our customers’ experience and engagement to build loyalty and meet their evolving needs?
- Philanthropy and Community Investment ─ How can we invest in initiatives that create positive social impact and contribute to community development?
- Health and Safety ─ How well are we ensuring our employees’ and stakeholders’ health and safety?
- Political and Regulatory Factors ─ How are we adapting to changes in political and regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance and minimize risk?
- Product Design and Circularity ─ How can we design and manage our products to enhance their circularity and minimize their environmental footprint?
1. Environmental Footprint
Considerations
The environmental footprint of a business refers to the impact that its activities have on the environment, including things like carbon emissions, water usage, and waste generation. This impact is important to consider because the planet’s health affects the health of the business. For example, climate change can disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and damage the reputation of a company. Also, taking action to reduce the environmental footprint can lead to cost savings and create opportunities for innovation and competitiveness. Plus, it’s just the right thing to do for the planet.
Key Impact Questions
Measuring a company’s environmental footprint is like taking a health check-up for the planet. To get an accurate picture of your company’s impact, it is essential to consider your resource usage, waste generation, emissions, and efforts to reduce your environmental impact. The answers to the following questions can help you identify areas for improvement and set goals for more sustainable practices:
- What are your company’s energy consumption levels and sources?
- How much water does your company use, and from what sources?
- What is the amount and type of waste your company generates?
- What is your company’s greenhouse gas emissions profile?
- How does your company’s operations impact local air quality?
- Does your company have any policies or programs in place to reduce its environmental impact?
- How transparent is your company about its environmental performance?
- What efforts are in place to reduce your company’s use of hazardous materials?
- Are there any green technologies or sustainable practices being implemented by your company?
- How does your company’s environmental performance compare to industry peers?
Key Performance Indicators
Here are some key performance indicators (KPIs) that businesses can consider to measure their progress in the environmental footprint dimension of the Impact Model:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Measure and track the total greenhouse gas emissions from your operations, including direct emissions, indirect emissions from purchased energy, and other indirect emissions.
- Energy Consumption: Monitor and reduce energy consumption by tracking total energy usage, identifying energy-intensive processes, and implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices.
- Water Consumption: Measure and manage water usage across your operations, identifying areas of high water consumption and implementing water-saving measures and technologies.
- Waste Generation: Track the amount of waste your business generates, classify waste types, and implement strategies to reduce waste generation, promote recycling, and minimize landfill disposal.
- Material Efficiency: Monitor and reduce the consumption of raw materials by implementing strategies like waste prevention, recycling, or using recycled or sustainable materials in product design and manufacturing.
- Biodiversity Impact: Assess and mitigate the impact of business activities on biodiversity, including habitat destruction, pollution, or the introduction of invasive species.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Evaluate and monitor the environmental performance of your supply chain partners, such as suppliers, distributors, and contractors, to ensure sustainable practices are followed throughout the value chain.
- Carbon Footprint of Products/Services: Calculate and disclose the carbon footprint associated with your products or services. This involves assessing the emissions associated with the entire lifecycle, including raw material sourcing, manufacturing, transportation, use, and end-of-life disposal.
- Sustainable Packaging: Measure and optimize packaging materials and design to reduce waste and environmental impact, considering recyclability, biodegradability, and renewable resources.
- Environmental Compliance: Ensure compliance with environmental regulations and standards, monitor any environmental incidents or violations, and track the number and severity of non-compliance.
These KPIs can help businesses track and measure their progress in reducing their environmental footprint and achieving sustainability goals. It is essential to customize these indicators based on the specific environmental aspects and impacts of your business and align them with relevant industry standards, guidelines, and international frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or ISO 14001.
2. Governance and Ethics
Impact Considerations
Governance and ethics are essential for shaping a business’s impact on stakeholders. Ethical governance involves transparency, accountability, stakeholder engagement, fair treatment, compliance, and responsible supply chain practices. Ethical decision-making should prioritize stakeholder well-being and avoid harm. Integrating CSR into governance positively impacts stakeholders, promoting social and environmental well-being. By prioritizing these considerations, businesses can shape their positive, responsible, and sustainable impact, fostering trust in the business ecosystem.
Key Impact Questions
- How do we ensure transparency and accountability in our business operations to build stakeholder trust?
- In what ways do we actively engage stakeholders in decision-making processes to consider their perspectives and interests?
- How do we ensure fair treatment and equality for all stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and local communities?
- Are we fully compliant with relevant regulations and laws to avoid negative repercussions for stakeholders?
- How do we monitor and assess the ethical implications of our supply chain, including labor and human rights standards, environmental practices, and fair trade principles?
- What mechanisms do we have to ensure ethical decision-making processes within our organization?
- How do we prioritize stakeholder well-being and avoid harm when weighing different options and evaluating potential impacts?
- To what extent do our governance practices incorporate corporate social responsibility initiatives to impact stakeholders and the wider community positively?
- How do we communicate and adhere to our organization’s ethical guidelines and values?
- Are we regularly evaluating and updating our governance and ethics practices to stay aligned with evolving societal expectations and emerging issues?
Key Performance Indicators
- Achievement of strategic objectives: Assessing the extent to which the business successfully meets its strategic goals and objectives, including those related to governance and ethical practices.
- Compliance program effectiveness: Measuring the compliance program’s effectiveness in ensuring adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies.
- Stakeholder engagement: Evaluating the level of stakeholder involvement and collaboration in decision-making processes, reflecting the commitment to ethical governance.
- Ethical culture and behavior: Monitoring and assessing the prevalence of ethical behavior throughout the organization, including factors like integrity, trust, and ethical decision-making.
- Reporting systems performance: Evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of governance and ethics reporting systems, such as whistleblower mechanisms or ethics hotlines.
- Risk management: Assessing the effectiveness of risk management processes, including the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks related to governance and ethics.
- Training and awareness programs: Measuring the impact and effectiveness of training and awareness programs focused on governance, ethics, and compliance topics.
- Non-compliance incidents: Tracking and analyzing the number and severity of non-compliance incidents to identify areas for improvement and risk mitigation.
- Supplier ethics and sustainability: Monitoring and measuring suppliers’ and supply chain partners’ ethical practices and sustainability performance.
- Corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives: Assessing the impact and outcomes of CSR initiatives, such as community investment, environmental sustainability, and diversity and inclusion efforts.
3. Social Impact
Impact Considerations
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
- Community Investment and Philanthropy
Key Impact Questions
- Who are the key stakeholders affected by the business endeavor?
- What are the social issues or challenges that the business endeavor aims to address?
- How does the business endeavor contribute to the local community and society?
- What steps has the business taken to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion in its operations and outcomes?
- How does the business endeavor engage and empower marginalized groups or communities?
- What environmental practices and initiatives does the business implement to minimize its ecological footprint?
- How does the business protect human rights and ensure fair labor practices throughout its operations and supply chain?
- What efforts does the business endeavor make to give back and support social causes or charitable organizations?
- How transparent is the business sharing its social impact and progress?
- What long-term goals or plans does the business have to improve its social impact continuously?
Key Performance Indicators
When measuring the tangible and intangible effects of efforts to improve social impact, several key performance indicators (KPIs) can be helpful. Here are some examples:
- Number of lives impacted: This quantifies the number of people benefiting from the business’s social initiatives, such as the number of individuals provided with education, healthcare, or employment opportunities.
- Financial investment in social initiatives: This KPI measures the financial resources allocated to improving social impact. It reflects the commitment of the business to prioritize social responsibility.
- Diversity and inclusion metrics: These KPIs assess the business’s efforts to foster diversity and inclusion within the workforce, such as measuring the percentage of women or underrepresented groups in leadership positions or tracking employee satisfaction and engagement levels.
- Environmental impact metrics: These KPIs gauge the business’s ecological footprint, including energy consumption, waste management practices, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, or initiatives implemented to promote sustainability.
- Social return on investment (SROI): SROI measures the social value generated relative to the resources invested. It quantifies the benefits created by social initiatives in monetary terms, allowing for comparisons and assessments of the effectiveness and efficiency of different projects.
- Customer sentiment and satisfaction: These metrics capture customer feedback and sentiment towards the business’s social initiatives. This includes customer perception of the business’s social responsibility efforts, willingness to support socially responsible companies, and overall customer satisfaction.
- Employee engagement and retention: These KPIs assess the impact of social initiatives on employee morale, satisfaction, and loyalty. Tracking metrics such as retention rates, employee volunteer participation, and employee feedback can provide insights into the effectiveness of the business’s social impact efforts.
It is important to note that KPIs should be tailored to the specific goals and initiatives of the business, ensuring they align with its mission and values. Regularly monitoring and analyzing these KPIs can help measure progress, identify areas of improvement, and drive continuous enhancements of the business’s social impact.
4. Financial Impact
Impact Considerations
The financial impact aspect of RoundMap’s Impact Model focuses on understanding the economic consequences of the organization’s activities on stakeholders and optimizing financial performance. It involves assessing the financial health and stability of the organization, ensuring equitable distribution of economic benefits, and managing financial risks. By prioritizing financial impact, RoundMap aims to achieve sustainable long-term growth and profitability while ensuring fair customer pricing, employee compensation, and responsible distribution of economic benefits to stakeholders. Through effective financial management practices, RoundMap can maximize its positive financial impact and minimize adverse outcomes, enabling it to drive positive change and create value for all stakeholders.
Key Impact Questions
- How do our business decisions impact the financial health and stability of the organization and its stakeholders?
- To what extent do our pricing strategies and practices ensure fair and competitive customer pricing while providing a reasonable profit margin for the organization?
- What measures are in place to ensure accurate and transparent financial reporting?
- Do we have robust risk management processes to identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks?
- How do we evaluate and manage the potential financial impact of regulatory changes or legal issues?
- Are we effectively managing our debt and leverage to maintain financial stability?
- How do we ensure fair compensation, benefits, and opportunities for growth for our employees?
- Are we effectively managing cash flow to ensure liquidity and meet the organization’s financial obligations?
- How do we allocate and distribute economic benefits to stakeholders, including employees, shareholders, suppliers, and local communities?
- Are we effectively managing and optimizing our financial resources for sustainable long-term growth and profitability?
Key Performance Indicators
When measuring the tangible and intangible effects of efforts to improve financial impact, several key performance indicators (KPIs) can be helpful. Here are some examples:
- Revenue growth and profitability: Assessing the organization’s ability to generate sustainable revenue growth and profitability over time.
- Gross profit margin: Monitoring the gross profit margin to assess the organization’s ability to generate profits after accounting for production costs.
- Cost control efficiency: Evaluating the organization’s ability to effectively manage and control costs to maximize financial performance.
- Debt-to-equity ratio: Assessing the organization’s leverage and debt levels relative to its equity, indicating its financial stability and risk exposure.
- Cash flow management: Monitoring and analyzing the organization’s ability to generate and manage cash flows to meet financial obligations.
- Employee compensation and benefits ratio: Measuring the proportion of revenue allocated to employee compensation and benefits to ensure fair and equitable distribution.
- Market share: Assessing the organization’s market share compared to competitors, indicating its competitiveness and financial impact.
- Return on Assets (ROA): Evaluating the financial return generated from the organization’s total assets, assessing its efficiency in resource utilization.
- Economic value added (EVA): Measuring the value created by the organization by exceeding the cost of capital, indicating its financial performance and added value.
Note: It is important to select the most relevant KPIs based on the industry, business model, and specific objectives of the organization.
5. Supply Chain Management
Impact Considerations
Supply Chain Management is a critical dimension of the Impact Model, encompassing the management of goods and services movement, sourcing, and production. Considering the impact of the supply chain is essential for environmental sustainability, social responsibility, risk management, reputation and branding, and cost efficiency. Organizations must analyze and optimize their supply chains to reduce environmental footprints, ensure fair labor practices, mitigate risks, meet customer expectations, and drive cost savings. Understanding and addressing the impact of the supply chain allows businesses to make informed decisions and align their practices with sustainability, ultimately leading to long-term success and positive impact.
Key Impact Questions
- How do we assess and track the environmental impact of our supply chain operations throughout the entire product lifecycle?
- Are there opportunities to optimize our supply chain to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, waste generation, and resource consumption?
- What measures do we have in place to ensure ethical sourcing and fair labor practices within our supply chain?
- How do we mitigate risks associated with potential disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters or supplier insolvency?
- Do we have clear visibility into our supply chain network and the ability to monitor and manage suppliers for compliance with our sustainability and social responsibility criteria?
- How can we enhance transparency and traceability in our supply chain to meet customer demands for responsible sourcing?
- Are there opportunities to collaborate with suppliers to improve sustainability practices, such as joint initiatives for reducing carbon emissions or waste?
- What strategies can we implement to reduce transportation-related environmental impacts, such as optimizing shipping routes or utilizing more sustainable modes of transportation?
- How do we engage with suppliers to promote and ensure adherence to our environmental and social responsibility standards?
- Are there technologies or innovations that can help us integrate sustainability considerations into our supply chain, such as blockchain for traceability or advanced analytics for demand forecasting?
Key Performance Indicators
Here are some Performance Indicators (KPIs) that can be used to measure progress in the supply chain management dimension of the Impact Model:
- Carbon Emissions: Measure and track the carbon footprint of the supply chain, including emissions from transportation, manufacturing, and energy consumption, to assess progress in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Monitor energy consumption within the supply chain to identify opportunities for energy efficiency improvements, such as optimizing production processes or utilizing renewable energy sources.
- Waste Generation: Track the amount of waste generated throughout the supply chain and set targets for waste reduction, encouraging the implementation of waste management strategies, recycling initiatives, and circular economy practices.
- Supplier Compliance: Assess the percentage of suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing and labor standards, such as certifications for fair trade, responsible mining, or responsible forestry, to ensure that the supply chain maintains high social responsibility standards.
- Supplier Diversity: Measure the inclusion of diverse suppliers within the supply chain, including minority-owned, women-owned, or local businesses, to promote diversity and inclusion in procurement practices.
- Supplier Performance: Evaluate supplier performance through metrics like on-time delivery, quality control, and customer satisfaction to ensure that the supply chain operates efficiently and effectively.
- Transparency and Traceability: Gauge the supply chain transparency and traceability level, such as the ability to track and document the origin and journey of raw materials, to ensure responsible sourcing and enhance customer trust.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Assess the capacity of the supply chain to handle disruptions and effectively recover from them, such as through metrics that measure response time to disruptions, downtime, and contingency planning.
- Cost Savings: Measure cost savings achieved through supply chain optimization, including reductions in transportation costs, inventory carrying costs, and overall operational expenses.
- Customer Satisfaction: Evaluate customer satisfaction and feedback related to the supply chain, such as order fulfillment, product availability, and delivery experience, to ensure customer expectations are met or exceeded.
These Performance Indicators provide a comprehensive framework for assessing and monitoring progress in supply chain management, enabling organizations to track and drive improvements that align with sustainability and impact goals.
6. Stakeholder Engagement
Impact Considerations
Stakeholder Engagement is a crucial element of the Impact Model, focusing on the active involvement and collaboration with stakeholders who have a vested interest or are affected by an organization’s operations, decisions, and impacts. Stakeholders can include employees, customers, local communities, investors, NGOs, government bodies, and more. Stakeholder engagement is essential for identifying, understanding, and managing the diverse perspectives, needs, and expectations of these stakeholders. It provides a framework to build trust, ensure transparency, gather feedback, and foster mutually beneficial relationships. Effective stakeholder engagement empowers organizations to make informed decisions, respond to societal concerns, create shared value, and drive positive impact in a long-term and sustainable manner.
Key Impact Questions
- Who are our key stakeholders, and what are their interests, concerns, and expectations regarding our organization’s activities, products, and impacts?
- How do we currently engage and communicate with our stakeholders? Are these channels effective, inclusive, and transparent?
- Are there any stakeholder groups that we are currently not engaging with or not prioritizing enough? How can we expand our stakeholder engagement efforts to ensure a more comprehensive approach?
- What mechanisms do we have in place to receive and integrate stakeholder feedback into our decision-making processes, strategy development, and impact assessment?
- How can we actively involve stakeholders in our sustainability initiatives and ensure their meaningful participation in shaping our goals, targets, and action plans?
- What efforts do we make to build and maintain trust with our stakeholders? How do we address any conflicts of interest or disagreements that may arise?
- How do we educate and raise awareness among our stakeholders about our sustainability commitments, progress, and the impact we are creating?
- Is there a process in place to assess the effectiveness of our stakeholder engagement efforts? How do we measure and evaluate the impact of our engagement strategies on stakeholder satisfaction and understanding?
- How can we leverage technology and digital platforms to enhance stakeholder engagement and promote more inclusive and real-time interactions?
- How do we report on our stakeholder engagement activities and outcomes to ensure transparency and accountability to both internal and external stakeholders?
Key Performance Indicators
Here are some potential KPIs to consider for measuring progress in the Stakeholder Engagement dimension of the Impact Model:
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Measure the level of satisfaction and engagement of stakeholders through surveys, focus groups, and other methods to assess the effectiveness of engagement efforts.
- Stakeholder Participation: Track the number and diversity of stakeholders participating in the engagement process, including the frequency and duration of engagement activities.
- Stakeholder Diversity: Monitor the diversity of stakeholder groups actively engaged in the engagement process to ensure that engagement efforts are inclusive and represent a broad range of perspectives.
- Issues Identification: Assess the number and types of issues stakeholders raise during the engagement process to identify areas of concern and develop strategies to address them.
- Feedback Utilization: Track the number and types of stakeholder concerns and feedback incorporated into decision-making processes, strategy development, and impact assessments.
- Transparency: Evaluate the level of transparency in stakeholder engagement activities, including the disclosure of engagement methods, objectives, and outcomes, to promote accountability and build trust with stakeholders.
- Partnership Building: Measure the development and strengthening of partnerships with stakeholders, such as collaborative initiatives, joint projects, and co-creation efforts, to promote mutually beneficial relationships.
- Social License: Assess the level of social acceptance and support for organizational activities and decisions in the communities in which they operate, to ensure that the organization has a “Social License to Operate” that aligns with stakeholder expectations.
- Materiality Assessment: Conduct a materiality assessment to identify the most significant risks and opportunities related to stakeholder engagement, prioritize engagement efforts, and set targets for improvement.
- Innovation: Evaluate the level of innovation in stakeholder engagement practices, such as using digital technologies, novel engagement methods, and creative problem-solving techniques, to drive more effective and efficient stakeholder engagement outcomes.
These KPIs provide a basis for organizations to monitor and measure the success of their stakeholder engagement efforts, evaluate the impact of these efforts on stakeholder relationships and organizational impact, and drive continuous improvement in this area.
7. Innovation
Impact Considerations
Innovation can have a significant impact on both businesses and their stakeholders. From a business perspective, innovation can drive growth, increase profitability, and improve competitiveness by creating new products, technologies, and business models that address customer needs and market gaps. It can also reduce costs, increase efficiency, and enhance the organization’s reputation as a thought leader.
Innovation can also have a positive effect on stakeholders by creating new opportunities, services, and experiences that improve their lives and generate social and environmental benefits. Stakeholders, such as customers and employees, are more likely to remain engaged and loyal to companies that offer innovative and high-quality products that meet their evolving needs. Additionally, innovation can create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and enhance the overall well-being of communities.
However, innovation can also negatively impact specific stakeholders, mainly if it is not managed responsibly. For example, suppose a business introduces a new product or technology that undermines the safety or security of customers or harms the environment. In that case, it may damage the company’s reputation and loyalty among stakeholders. Similarly, if innovation leads to job losses or reduces the quality of life in communities, it may create resentment or resistance from specific stakeholder groups.
Key Impact Questions
- How does innovation contribute to the growth and competitiveness of our business? What specific innovations have we pursued or are planning to pursue?
- What are the potential benefits of these innovations for our customers, employees, and other stakeholders? How will these innovations improve their experiences, meet their needs, or address their challenges?
- Are there any potential risks or unintended consequences associated with our innovations? How can we proactively identify and mitigate these risks to ensure a positive impact on stakeholders?
- How do our stakeholders perceive our approach to innovation? Are they aware of and supportive of our innovative initiatives?
- How can we involve our stakeholders in the innovation process to ensure that their perspectives and feedback are considered? How do we actively engage them in co-creation, testing, or gathering ideas for future innovations?
- What steps are we taking to communicate the value and benefits of our innovations to our stakeholders? How can we improve our communication channels and messages to ensure they understand the positive impact our innovations can have on them?
- How does our innovation strategy align with our organizational values and sustainability goals? Are we considering social and environmental factors in our innovation process to maximize positive impact and minimize negative externalities?
- Are there any specific stakeholder groups our innovative initiatives might disproportionately impact? How can we ensure that we take their needs and concerns into consideration and address any potential inequalities or adverse effects?
- How can we measure and evaluate the impact of our innovations on various stakeholder groups? Are there specific metrics or indicators that we can use to assess the effectiveness and success of our innovation initiatives?
- How can we foster a culture of innovation within our organization and among our stakeholders? How can we encourage and reward creativity, risk-taking, and collaboration to drive positive impact through innovation?
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress in the planned impact of innovation can be challenging, but organizations need to assess the effectiveness of their efforts. Here are some approaches and key performance indicators (KPIs) to consider when measuring progress in the planned impact of innovation:
- Revenue and Profitability: Measure the financial impact of innovation by tracking metrics such as revenue growth, profit margins, and return on investment (ROI) for innovative products or initiatives. This helps determine if the planned impact on business growth and financial performance is being achieved.
- Market Share: Evaluate the impact of innovation on market share by monitoring changes in market share metrics, such as percentage of market sales or customer acquisition rates. This can indicate if the planned impact of innovation in terms of market competitiveness and growth is being realized.
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure the impact of innovation on customer satisfaction through surveys, feedback, and customer loyalty metrics. This helps assess if the planned impact of innovation in terms of improved customer experiences and meeting customer needs is being achieved.
- New Product Adoption: Track the adoption rate of new products or services resulting from innovation to evaluate market acceptance and impact on customer behavior. This helps determine if the planned impact of innovation in terms of product adoption and market penetration is being realized.
- Speed of Innovation: Measure the time it takes to bring new ideas, products, or solutions to market to assess the impact of innovation on the organization’s ability to respond quickly to market demands and stay ahead of competitors.
- Employee Engagement and Productivity: Evaluate the impact of innovation on employee engagement and productivity through surveys, performance indicators, and employee feedback. This helps determine if the planned impact of innovation in terms of fostering a culture of innovation and empowering employees is being achieved.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Measure the number and quality of partnerships or collaborations formed due to innovative initiatives to assess the impact on strategic alliances, market access, and knowledge sharing, which can contribute to long-term growth and impact.
- Patents and Intellectual Property: Monitor the number of patents filed or intellectual property generated due to innovation to assess the planned impact on building intellectual capital and creating competitive advantages.
- Social and Environmental Impact: Evaluate the impact of innovation on social and environmental factors by tracking relevant KPIs, such as reduction in carbon footprint, positive social contributions, or increased sustainability metrics.
- Innovation Metrics: Develop specific metrics to measure progress in the planned impact of innovation, such as the number of new ideas generated, successful product launches, cost savings, or process improvements resulting from innovative initiatives. These metrics should align with the organization’s innovation strategy and goals.
It’s essential to customize the measurement approach and KPIs based on the specific objectives, context, and industry of the organization. Regularly reviewing and analyzing these indicators can provide insights into the progress and effectiveness of innovation efforts and enable organizations to make data-driven decisions to enhance their impact.
8. Technology and Digitalization
Impact Considerations
Technology and digitization have a profound impact on businesses and their stakeholders. From a business perspective, technology and digitization enable companies to streamline operations, increase efficiencies, and reduce costs. They can also create new business opportunities, develop innovative products and services, and reach new customers through digital marketing and e-commerce channels.
Furthermore, technology and digitization can potentially transform entire industries by disrupting traditional business models and creating new ones. For example, the rise of fintech has enabled consumers to access financial services online, changing how banking and financial services are provided. Similarly, the emergence of ride-sharing services has disrupted the traditional taxi industry and offered consumers more choices for transportation.
For stakeholders such as customers and employees, technology and digitization have enabled greater connectivity, convenience, and personalization. Customers can access products and services anytime and anywhere, while employees can work from anywhere and collaborate virtually with colleagues in real time. This can lead to improved customer experiences, increased employee productivity, and greater flexibility and work-life balance.
However, the impact of technology and digitization on specific stakeholders can also present challenges, particularly those who may be less digitally literate or have limited access to technology. This can lead to a digital divide, where certain groups are excluded from the benefits of digitalization, such as access to e-commerce or remote work opportunities. There may also be concerns about job displacement or data privacy and security.
To realize the full potential of technology and digitization, businesses must engage in responsible practices that address these challenges and prioritize the needs of their stakeholders. This includes investing in digital infrastructure to ensure broader access to technology, providing digital skills training and support to employees, and implementing solid data privacy and security policies.
Key Impact Questions
- How has technology and digitalization transformed our industry or sector? What are the key digital trends and innovations that are disrupting or shaping our business?
- How are we utilizing technology and digital tools to improve our operational efficiency and productivity? Are we automating processes, implementing digital platforms, or utilizing data analytics to optimize our business operations?
- What new opportunities or business models have emerged as a result of technology and digitalization? Are we exploring new revenue streams, partnerships, or market expansion possibilities enabled by digital solutions?
- How are we leveraging digital channels and platforms to enhance our customer experience? Are we utilizing social media, mobile applications, or personalized marketing strategies to connect with and serve our customers more effectively?
- How can we leverage data and analytics to gain actionable insights and make informed business decisions? Are we collecting, analyzing, and utilizing data to improve our products, services, and overall business performance?
- How are we preparing our workforce for the digital future? Are we providing training and upskilling opportunities for our employees to adapt to technological changes and embrace digital tools in their roles?
- What cybersecurity measures do we have in place to protect our business and customer data? Are we implementing robust security protocols, conducting regular risk assessments, and staying up to date on industry best practices for cybersecurity?
- How are we managing the ethical and social implications of technology in our business? Are we mindful of issues like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and digital divide, and taking steps to address them in our operations and decision-making?
- How can technology and digital solutions contribute to our sustainability goals? Are we leveraging digital tools to reduce our environmental footprint, minimize waste, and promote sustainable practices in our business operations?
- How are we staying ahead of technological advancements and digital disruptions in our industry? Are we continuously scanning the technological landscape, monitoring industry trends, and engaging with external partners or experts to ensure our business remains innovative and competitive?
Key Performance Indicators
Here are some key performance indicators (KPIs) that businesses can consider to measure progress in the impact dimension of technology and digitalization:
- Digital Revenue Growth: Measure the percentage increase in revenue generated through digital channels such as e-commerce platforms, online marketplaces, or digital subscriptions.
- Website Traffic: Track the number of visits and unique visitors to your website. This can help gauge the effectiveness of online marketing efforts and the overall digital presence.
- Conversion Rate: Calculate the percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a lead form. This indicates the effectiveness of your website in driving customer engagement and conversions.
- Customer Engagement: Monitor metrics such as time spent on your website or social media platforms, number of comments or shares, or email open and click-through rates. These metrics indicate the level of customer engagement and interaction with your digital content.
- Customer Satisfaction: Utilize customer satisfaction surveys or feedback mechanisms to measure customer satisfaction with your digital channels, products, or services. This can help gauge the impact of technology on customer experience and loyalty.
- Digital Reach: Assess the size and growth of your digital audience across various platforms such as social media followers, email subscribers, or mobile app downloads. This reflects the reach and impact of your digital presence.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Analyze metrics such as process cycle time, cost per transaction, or labor productivity to measure the efficiency gains and cost savings achieved through technology and digitalization initiatives.
- Innovation and New Product Development: Evaluate the number of new digital products or services launched, the percentage of revenue generated from new products, or customer feedback on the value and impact of these innovations.
- Employee Productivity and Satisfaction: Measure employee satisfaction and productivity with digital tools and technologies. This can be assessed through surveys, employee feedback, or efficiency metrics related to digital workflows.
- Cybersecurity Metrics: Monitor cybersecurity metrics such as the number of security incidents, time to detect and respond to threats, or the success rate of cybersecurity awareness training. This helps assess the effectiveness of your cybersecurity measures.
These KPIs can help businesses track and measure their progress in leveraging technology and digitalization to achieve desired outcomes and impact. It is important to customize these indicators to align with your specific business goals, priorities, and industry dynamics.
9. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Impact Considerations
The Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) dimension of the Impact Model of RoundMap is critical for businesses and their stakeholders for several reasons. A diverse and inclusive workplace can lead to greater creativity, innovation, and problem-solving, as individuals with different backgrounds and perspectives bring unique insights and ideas. Diversity, equity, and inclusion also enhance employee engagement and productivity, as employees feel valued, respected, and supported, leading to greater job satisfaction and reduced turnover.
In addition to the internal benefits for businesses, DEI can also have a positive impact on external stakeholders, such as customers and the broader community. Research has shown that diverse and inclusive businesses are more likely to attract and retain a diverse customer base and outperform their competitors financially. Moreover, businesses that value diversity, equity, and inclusion can help promote social justice and reduce inequality in their communities.
Key Impact Questions
Here are ten questions that can help businesses assess, mitigate, or optimize the impact of the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) dimension:
- How diverse is our workforce regarding race, ethnicity, gender, age, abilities, and other dimensions of diversity? Are there any gaps or underrepresented groups?
- What efforts are we making to ensure equal employment opportunities and eliminate biases in recruitment, hiring, and promotion processes?
- Do we have policies and practices to foster an inclusive and respectful work environment? How do we ensure all employees feel valued, respected, and included?
- Are there any barriers or challenges that employees from underrepresented groups face within our organization? How can we address and overcome these barriers?
- Are our compensation and benefits systems fair and equitable, considering factors such as gender, race, and other diversity dimensions?
- How do we provide ongoing training and development opportunities to promote diversity and inclusion awareness, cultural competence, and the understanding of unconscious biases?
- Are there mechanisms for employees to raise concerns or report incidents related to diversity, equity, and inclusion? How do we ensure accountability and a fair resolution process?
- Do our leadership and management teams reflect the diversity of our workforce and stakeholders? If not, what actions can we take to enhance senior-level diversity?
- Are we promoting and supporting employee resource groups or affinity groups to foster a sense of belonging and support for underrepresented employees?
- How do we engage with our customers, suppliers, and the wider community to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion? Are there any partnerships or initiatives we can undertake to drive positive change?
These questions can help businesses reflect on their current practices, identify areas for improvement, and develop strategies and initiatives to enhance the impact of diversity, equity, and inclusion within their organization. It is essential to involve diverse stakeholders, including employees, in these discussions and continuously evaluate and monitor progress towards DEI goals.
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress in the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) dimension requires tracking and analyzing several Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Here are ten KPIs that can help businesses assess, monitor, and improve their DEI impact:
- Diversity Index: Track and report the percentage of employees in different demographic categories, including gender, race, ethnicity, age, sexual orientation, and abilities, to assess workforce diversity levels.
- Inclusion Index: Measure and report on employee perceptions of the inclusivity of the workplace, including factors such as belongingness, respect, and support.
- Employee Satisfaction: Measure and track employee engagement levels and job satisfaction, broken down by demographic categories, to assess the impact of DEI efforts on morale.
- Turnover Rates: Compare the turnover rates for different demographic categories to identify any disparities and understand the reasons for turnover.
- Representation in Leadership: Track and report representation of underrepresented groups in leadership and management positions, including C-suite and board members.
- Pay Equity: Analyze and report the gender and race pay gap at different organizational levels to ensure equitable pay. There are no disparities based on gender or race.
- Training and Development: Measure and track the number of employees who have completed DEI training, including unconscious bias and cultural competence training.
- Talent Development: Track and report on opportunities for career development and advancement available to employees at different organizational levels.
- Employee Resource Groups (ERGs): Measure employee participation in ERGs, the number of ERGs, and the events and initiatives conducted by ERGs to promote a sense of belonging and community.
- Community Engagement: Measure and report on your organization’s engagement with the community, including outreach to underrepresented groups, partnerships with community organizations, and DEI-focused philanthropy efforts.
These KPIs can help businesses measure the effectiveness of their diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives, identify areas for improvement, and track progress toward DEI goals. Customizing these KPIs for the business’s specific needs and tracking them regularly can help businesses create more diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces, positively impact employee engagement, retention, and productivity, and ultimately lead to better business results.
10. Customer Experience and Engagement
Impact Considerations
The Customer Experience and Engagement dimension refers to the interactions, perceptions, and overall satisfaction that customers have with a business or brand. It encompasses every touchpoint and interaction a customer has, from the initial contact to ongoing engagement and support. This dimension is crucial for businesses as it directly influences customer satisfaction, loyalty, and brand reputation.
In today’s competitive market, businesses must prioritize providing exceptional customer experiences to stand out. A positive customer experience can increase customer loyalty, repeat purchases, and positive word-of-mouth referrals. On the other hand, a poor customer experience can result in customer dissatisfaction, negative reviews, and a loss of business.
Customer engagement is another vital aspect of this dimension. Engaged customers are actively involved with a brand, show loyalty, and willingly participate in interactions or transactions. Effective customer engagement strategies foster strong relationships, encourage customer feedback, and promote brand advocacy.
By focusing on the Customer Experience and Engagement dimension, businesses can build a positive brand reputation, gain a competitive advantage, and drive revenue growth. By understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points, businesses can better tailor their products, services, and interactions to meet and exceed customer expectations.
Key Impact Questions
Here are ten questions to ask while assessing, planning, or improving the impact of your business on the Customer Experience and Engagement dimension:
- How are we measuring and monitoring customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement?
- What are the most significant pain points or challenges customers face while interacting with our business or brand, and how are we addressing them?
- How personalized are our interactions with customers? Are we tailoring our products, services, and communications to meet individual customer needs?
- Are we delivering a seamless and consistent experience across all customer touchpoints, including online, mobile, in-person, and customer service channels?
- How are we proactively engaging with customers to understand their feedback and preferences, and how are we using that information to improve our offerings?
- How are we leveraging technology, tools, and data analytics to improve the customer experience and engagement?
- Are we providing customers with quick and efficient support, and are we resolving their issues and concerns in a timely and satisfactory manner?
- How are we communicating with customers about new products, services, or updates, and are we doing so in a way that is relevant and engaging to them?
- Are we creating opportunities for customers to interact with our brand beyond purchasing, such as through communities, social media, or events?
- How are we promoting and encouraging customer advocacy and word-of-mouth referrals, and are we recognizing and rewarding loyal customers?
Asking these questions can help businesses assess their current impact on the Customer Experience and Engagement dimension, plan for improvements, and ultimately ensure that they provide exceptional experiences that lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue growth.
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress and success in the Customer Experience and Engagement dimension requires setting and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs). Here are some KPIs to consider:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty by asking customers how likely they are to recommend a brand or product to others. The score ranges from -100 to 100, with a higher score indicating greater customer loyalty.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): CSAT measures customer satisfaction with a particular interaction, experience, or product. It usually involves a survey asking customers to rate their satisfaction on a scale of 1-5 or 1-10.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): CES measures how much effort customers need to put into a specific interaction or task, such as finding information or resolving an issue. It usually involves a survey asking customers to rate the effort required on a scale of easy to difficult.
- Repeat Customer Rate: This metric measures the percentage of customers who make repeat purchases or engage with a brand repeatedly over a specific period.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV measures the total value a customer brings to a business over their lifetime. A higher CLV indicates that customers stay loyal to a business, make repeat purchases, and have a high overall value.
- First Response Time (FRT): FRT measures how quickly a business responds to customer inquiries or issues via email, phone, or live chat. A faster FRT is usually an indicator of good customer service.
- Churn and Retention Rates: The churn rate measures the percentage of customers who stop doing business with a brand over time, while the retention rate measures the percentage of customers who continue to do business with a brand.
These KPIs provide a quantitative way to measure progress in the Customer Experience and Engagement dimension. By setting realistic targets and tracking these metrics regularly, businesses can understand which areas need improvement, refine their strategies, and ultimately provide a better customer experience.
11. Philanthropy and Community Investment
Impact Considerations
The Philanthropy and Community Investment dimension of the Impact Model has significant considerations for both businesses and their stakeholders. Engaging in philanthropic activities and community investment allows businesses to enhance their reputation, build stronger relationships with stakeholders, and demonstrate commitment to social responsibility. It can positively impact employee morale, attract and retain talent, and contribute to sustainable development goals.
Additionally, these initiatives can create long-term value by differentiating the business, driving growth, and fostering collaboration and partnerships with other organizations. By actively considering the impact of philanthropy and community investment, businesses can make a positive difference in society while also benefiting their stakeholders and ensuring a sustainable future.
Key Impact Questions
Here are ten questions to ask when assessing, mitigating, or optimizing the impact of the Philanthropy and Community Investment dimension on the business and its stakeholders:
- How aligned are our philanthropic initiatives with our business values and strategic goals?
- Are we effectively communicating our philanthropic efforts and their impact to our stakeholders?
- How are we engaging our employees in our philanthropic initiatives and fostering a sense of shared purpose?
- Are our philanthropic activities and community investments addressing the most pressing social issues relevant to our industry and communities?
- How are we measuring and evaluating the effectiveness and impact of our philanthropic initiatives?
- Are our philanthropic efforts inclusive and respectful of the diversity of the communities we serve?
- Are we collaborating and partnering with relevant organizations to maximize the impact of our philanthropic initiatives?
- How do we involve our stakeholders, including employees, customers, and local communities, in the decision-making process for our philanthropic efforts?
- Are we considering the long-term sustainability and scalability of our philanthropic initiatives?
- What steps are we taking to ensure transparency and accountability in our philanthropic and community investment activities?
These questions can help businesses critically assess and optimize their philanthropy and community investment initiatives, mitigate negative impacts, and align them with the overall business strategy and stakeholder expectations.
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress in the Philanthropy and Community Investment dimension of the Impact Model requires tracking and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the organization’s philanthropic activities and community investment efforts. Here are some common KPIs to consider:
- Dollars and Hours Donated: This measures the amount of money, resources, or volunteer hours donated to charitable causes or community initiatives.
- Social Impact: This KPI measures the impact of philanthropic initiatives and community investment on the social or environmental aspect represented, such as education, healthcare, poverty alleviation, environmental conservation, or disaster relief.
- Employee Engagement: This measures employee involvement in philanthropic and community investment initiatives, such as volunteer participation rates or feedback survey results.
- Stakeholder Feedback: This measures the feedback from stakeholders, such as customers, investors, or local communities, regarding the impact and effectiveness of philanthropic and community investment initiatives.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: This measures the number and quality of partnerships and collaborations established with nonprofit organizations, government entities, or other businesses to maximize the impact of philanthropic efforts.
- Reputation Score: This KPI measures a business’s reputation in terms of social responsibility and community involvement, which can be tracked through surveys, reviews, or social media sentiment analysis.
- Impact on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): This measures the alignment of philanthropic and community investment initiatives with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and progress towards achieving them.
By setting realistic targets, tracking these KPIs regularly, and evaluating progress against them, businesses can understand which areas of their philanthropic and community investment initiatives need improvement, refine their strategies, and ultimately provide a better social impact while aligning with their stakeholders’ expectations.
12. Health and Safety
Impact Considerations
The Health and Safety dimension of the Impact Model is crucial for businesses to prioritize the well-being of their employees, customers, and other stakeholders. When aiming to improve or mitigate the impact of this dimension, several considerations come into play. Firstly, businesses need to prioritize creating a safe and healthy work environment, which includes implementing proper safety protocols, providing necessary training, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. It also involves actively identifying and mitigating workplace hazards and risks.
Additionally, businesses should focus on promoting the physical and mental well-being of their employees through initiatives such as wellness programs, flexible work arrangements, and access to healthcare resources. Engaging stakeholders and obtaining feedback on health and safety practices is essential to ensure continuous improvement and address concerns. By prioritizing health and safety, businesses can foster a positive work culture, enhance productivity, and build stakeholder trust.
Key Impact Questions
- How effective is our health and safety policies and procedures in preventing workplace accidents and injuries?
- Are we providing adequate training and resources to ensure employees understand and follow health and safety protocols?
- How are we identifying and addressing potential hazards or risks in the workplace, such as ergonomic issues, chemical exposures, or safety hazards?
- Are we regularly conducting health and safety audits and inspections to assess compliance and identify areas for improvement?
- How are we promoting and supporting the physical and mental well-being of our employees, such as through wellness programs and initiatives?
- Are we actively involving employees in the development and implementation of health and safety policies and programs?
- How are we monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of our health and safety initiatives?
- Are we providing the necessary resources and support to ensure a safe and healthy work environment for all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and visitors?
- How well do we communicate and educate stakeholders about health and safety practices, procedures, and expectations?
- Are we prepared for emergencies and crises, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies, and do we have a crisis management plan?
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress in the Health and Safety dimension of the Impact Model requires tracking and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of health and safety practices. Here are some common KPIs to consider:
- Incident Rate: This measures the number of workplace accidents, injuries, or illnesses per unit of time, allowing you to track any changes in the frequency and severity of incidents.
- Lost Time Injury Rate (LTIR): This measures the number of work-related injuries or illnesses that result in time away from work per unit of time, providing insights into the impact of incidents on employee well-being and productivity.
- Near Miss Reporting: This tracks the number of near-miss incidents reported, indicating potential hazards or risks that must be addressed to prevent future accidents.
- Employee Training Participation: This measures the percentage of employees who participate in and complete health and safety training programs, indicating the level of awareness and engagement in the workplace.
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys: This assesses employee perceptions of health and safety practices and programs, providing insights into the effectiveness of existing measures and identifying areas for improvement.
- Compliance with Regulations: This measures the organization’s compliance with relevant health and safety regulations and standards.
- Safety Inspections and Audits: This quantifies the frequency and outcome of safety inspections and audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Return on Investment (ROI): This measures the financial impact of health and safety initiatives, such as reduced medical costs, insurance premiums, and productivity gains.
- Health Promotion Program Participation: This measures employee participation in health promotion programs, such as wellness challenges or fitness activities, to gauge the extent to which employees actively engage in activities that promote their well-being.
- Absenteeism and Sick Leave: This tracks the frequency and duration of employee absenteeism and sick leave, providing insights into the overall health and well-being of the workforce.
By regularly evaluating and monitoring these KPIs, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their health and safety initiatives, identify areas for improvement, and take proactive measures to enhance the well-being of their employees and stakeholders continuously.
13. Political and Regulatory Factors
Impact Considerations
The Political and Regulatory Factors dimension encompasses the impact of laws, regulations, and government policies on the business and its stakeholders. Businesses must consider the potential impacts to navigate the legal and regulatory environment effectively. From a business standpoint, political and regulatory factors can significantly influence operations, market access, and profitability. Changes in laws or regulations can create new opportunities or pose challenges that require adaptation and compliance.
Businesses must be aware of and compliant with relevant laws and regulations to mitigate legal and reputational risks. Additionally, political and regulatory factors can affect stakeholders such as customers, employees, and investors. It is essential to consider how changes in the political landscape or new regulations may impact stakeholders’ rights, privacy, safety, or access to products and services. By proactively monitoring and adapting to political and regulatory factors, businesses can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and maintain trust and compliance with stakeholders.
Key Impact Questions
- What laws and regulations govern our industry, and how do they impact our operations, products, and services?
- How have recent changes in laws, regulations, or government policies affected our business, and what are the implications for our stakeholders?
- Are we proactively monitoring and assessing potential changes in laws, regulations, or government policies to understand their potential impact on our business and stakeholders?
- Do we have a compliance program in place to ensure that we are meeting legal and regulatory requirements?
- How do we communicate changes in laws, regulations, or government policies to our stakeholders, and how do we ensure they know their rights and responsibilities?
- How do we ensure that the personal data and sensitive information of our stakeholders are protected following relevant regulations?
- Are we engaging with policymakers and regulatory authorities to provide input into developing laws and regulations that affect our industry?
- How do we manage and mitigate the risk of reputational damage associated with non-compliance with laws and regulations?
- How do we ensure that our stakeholders have access to the products and services they need, even in the face of legal or regulatory challenges?
- Do our policies and practices reflect ethical standards beyond compliance with laws and regulations?
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress in the Political and Regulatory Factors dimension can be challenging, as it involves assessing compliance, regulatory changes, and stakeholder perceptions. However, here are some key performance indicators (KPIs) that can help measure progress in this dimension:
- Compliance Score: This measures the extent to which the business complies with relevant laws and regulations. It can be tracked through audits, self-assessments, and legal reviews.
- Regulatory Risk Assessments: This evaluates the business’s ability to identify and assess potential risks from regulation changes or government policies.
- Stakeholder Perception Surveys: This measures stakeholders’ perceptions of the organization’s compliance with laws and regulations and their overall satisfaction with the company’s approach to political and regulatory factors.
- Regulatory Violations: This tracks the number and severity of regulatory violations or fines received by the business, indicating the level of compliance and potential areas for improvement.
- Policy Engagement Metrics: This measures the extent of the business’s engagement with policymakers, such as the number of consultations attended, policy submissions made, or collaborative efforts with regulatory authorities.
- Regulatory Change Monitoring: This assesses the business’s ability to effectively monitor and anticipate changes in laws, regulations, and government policies that may impact its operations.
- Privacy and Data Protection Compliance: This tracks compliance with data protection regulations, such as the number of data breaches, privacy complaints, and implementation of privacy-enhancing measures.
- Regulatory Approvals or Permits: This measures the time taken to obtain necessary regulatory approvals or permits, indicating the efficiency of regulatory compliance processes.
- Litigation and Legal Disputes: This quantifies the number and impact of legal disputes related to regulatory matters, such as lawsuits or legal settlements.
- Regulatory Compliance Training Participation: This measures the extent of employee participation in training programs related to legal and regulatory compliance, indicating the level of awareness and education in the organization.
By monitoring these KPIs, businesses can track their progress in complying with laws and regulations, manage risks associated with political and regulatory changes, and ensure that stakeholders’ concerns are addressed. It’s important to customize these KPIs based on the specific industry, regulatory context, and business objectives of the organization.
14. Product Design and Circularity
Impact Considerations
The Product Design and Circularity dimension focuses on the impact of the product design and lifecycle on the business and its stakeholders. It involves considering the environmental, social, and economic aspects of product design, production, use, and end-of-life management.
Businesses must consider the sustainability and circularity of their products to minimize negative environmental impacts, reduce waste, optimize resources, and meet the changing expectations of stakeholders. In terms of impacts, businesses and stakeholders should consider how product design and circularity affect resource consumption, emissions, waste generation, product lifespan, customer satisfaction, and stakeholder trust.
A well-designed and circular product can enhance resource efficiency, promote sustainable consumption, reduce environmental footprints, minimize waste management costs, and improve brand reputation. It can also provide value to customers through durability, recyclability, modularity, and repairability. Businesses should factor in stakeholder perspectives, align their product design with sustainability objectives, and consider the interests of customers, employees, suppliers, regulators, and local communities to ensure a holistic approach to product design and circularity.
Key Impact Questions
- How can our products be designed for optimal circularity and sustainability in their production, use, and end-of-life phases?
- Are we considering the entire lifecycle of our products, including their carbon footprint, resource use, and waste generation, in our design and production processes?
- How can we encourage sustainable consumption and reduce waste through product design and promotion?
- Are our products designed with social and cultural considerations in mind, such as the fair treatment of workers and respect for cultural practices?
- How can we design our products to be recyclable, reusable, or upgradable, reducing their environmental impact?
- What steps can we take to reduce the amount of waste generated by our products during production or at the end of their life?
- How can we collaborate with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders to promote sustainable and circular design practices?
- Are we transparent about the environmental and social impacts of our products with our stakeholders?
- How are consumers responding to our products, and what kind of feedback can we expect related to our product design?
- How can we work with policymakers and regulatory bodies to promote circularity and sustainability across the industries we operate in?
Key Performance Indicators
Measuring progress in the Product Design and Circularity dimension can be challenging as it involves assessing the entire lifecycle of the product design, production, usage, and end-of-life management. However, here are some key performance indicators (KPIs) that can help measure progress in this dimension:
- Recyclability rate: This measures the amount of material that is recovered and recycled at the end of a product’s life, indicating the product’s circularity.
- Material efficiency: This measures the amount of input materials required to produce a unit of output, indicating resource efficiency in the production process.
- Carbon footprint: This measures a product’s greenhouse gas emissions throughout its lifecycle, reflecting its environmental impact.
- Product lifespan: This measures the number of years or uses a product has before it is discarded, indicating its durability.
- Packaging waste: This measures the amount of product packaging waste generated throughout the product’s lifecycle, indicating packaging circularity.
- Repairability: This measures how easily a product can be repaired, prolonging its lifespan and reducing waste.
- Water footprint: This measures the amount of water used to produce a product throughout its lifecycle, reflecting the product’s environmental impact.
- Sales of sustainable products: This measures the percentage or volume of sales from sustainable or circular products.
- Material substitution: This measures how sustainable materials are substituted for less sustainable ones in the product design and production process.
- Stakeholder satisfaction: This measures the satisfaction level of stakeholders, such as customers, employees, suppliers, and regulators, with the sustainability and circularity of the product.
By monitoring these KPIs, businesses can track their progress in meeting sustainability and circularity objectives, reduce waste, and optimize resource utilization while meeting stakeholder expectations. It’s important to customize these KPIs based on the industry, product, and stakeholder context and define performance targets periodically to drive continuous improvement.
Matching the Impact Dimensions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Alternatively, we can match the Impact Dimensions with the relevant Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmental Footprint
- Product Design and Circularity
- Technology and Digitalization
Aligned with:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- Social Responsibility and Stakeholder Engagement
- Social Impact
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Philanthropy and Community Investment
- Stakeholder Engagement
Aligned with:
- SDG 1: No Poverty
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- SDG 5: Gender Equality
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Organizational Ethics and Governance
- Governance and Ethics
- Political and Regulatory Factors
Aligned with:
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- Operational Excellence and Risk Management
- Financial Impact
- Supply Chain Management
- Innovation
- Health and Safety
Aligned with:
- SDG 1: No Poverty
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
This framework aligns the Impact Dimensions with the relevant SDGs, ensuring that a comprehensive and holistic approach to sustainability is taken. It also guides how to group sustainability dimensions into related categories to help identify focus areas for sustainability initiatives and facilitate stakeholder communication.